FORM 4 GEOGRAPHY 2019 ANSWERS
PART ONE:- MULTPLE CHOICE
| 1 | A |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | A |
| 5 | A |
| 6 | D |
| 7 | C |
| 8 | C |
| 9 | C |
| 10 | B |
PART TWO:- MATCHING
| 1 | F |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | G |
| 4 | I |
| 5 | H |
| 6 | B |
| 7 | A |
| 8 | J |
| 9 | E |
| 10 | D |
PART:- THREE
1) A. Geography is the scientific study of the earth as a home of humankind. It is the relationship between physical and human phenomena on the earth’s surface.
B. I) Human Geography
II) Physical Geography
III) Economic Geography
2) A. weather is the atmospheric condition of a place of a particular time which observes short period of time.
B. I) MMT= 7200c /30= 240c
II) Tuesday
III) Saturday= 300 and Monday= 300
3) I) R
II) P
III) S and Q
IV) T
4) A) Communication is the process of transferring information from one person or place to another and receiving of feedback.
B)
r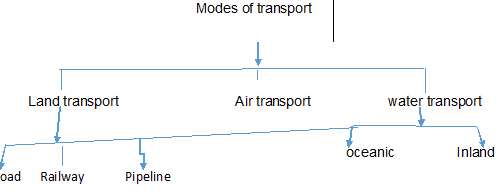
c) I) Human porterage are carrying of goods by people on their backs, heads, shoulders and hands.
II) Donkey, Camels, Horses, Elephants and E.T.C.
5) A) Cottage industry are small scale industry which runs by members of the same family for creation of products and services.
B)
| Level of production | Industries |
| A) Extracting | Primary industry |
| B) Processing | Secondary industry |
| C) Service | Tertiary industry |
C) Significance of industry.
-
- it creates employment opportunities for people
- it serves as a source of income improves living stander
- saves the country foreign exchange through reduction in manufactured goods that are imported
- it has encourages balance population distribution
- it has encourages development of infrastructure
- it has encourages effective exploitation of mineral resources
- it encourages the productivity use of local available materials and resources
6) A) Climate change is the long term changes in the weather pattern in a region.
B) Consequence of climate change
-
- Melting of ice
- Desertification
- Scare of water:- decreasing availability of water resource
- Sea level rise:- this can lead to floods
- Contaminating coastal fresh water sources
- Extreme high and low temperature
- Higher of heavy rainfall
- Loss of biodiversity
- Healthy risk from rising heat wave.
7) A) Mining is the process of extracting valuable minerals both solid and liquid from the earth crust which forms economic interest.
-
- Abundance of the mineral: Mining depends on the overall cost of mining compared to the market price of the mineral.
- Value of the mineral: Some minerals are very valuable so that even smaller quantities may justify their extraction.
- Method of mining: Some mining methods are very costly, where the deposits are very deep underground and in difficult landscape.
- Market reliability: Markets for some minerals are not always reliable. Sometimes, prices for certain minerals fluctuate in international markets and this reduces the profits from mining and makes mining for such minerals unprofitable.
8) A) 1cm represent 4km
B) 416km2
9) A) I) Dispersal settlement
II) Linear settlement
III) Nucleated settlement
B) Factors influencing settlement
-
- Suitable climate: rainfall and temperatures determine settlement and the occupation by various people
- Relief: settlements are attracted to places where the land is flat and undulating like plateaus and coastal plains.
- Fertile soils: areas with fertile, well-drained soils attract human settlements e.g. Jubba and Shebelle banks.
- Absence of pests and diseases: human beings require a healthy environment, without pests and diseases.
- Water supply: settlements need water, they often locate on wet point sites for this.
- Defense: people prefer to settle in places that are free from dangerous animals and enemies.
- Political factors: some areas are designed and developed as settlements by the government.
- Communications: settlements often located next to rivers that could be easily crossed. These are called bridging points. Other favorable places included where at the junctions of valleys or in gaps through hills.
10) A) NMR= 3.75
B) GMR= 8.75
PART FOUR:- EXTENDED
1) A) Ground general view
B) Wildlife and tourism
C) Factors that favour development of the major activity in wildlife and tourism.
-
- Forests. Areas that receive high rainfall and have fertile soils enable the growth of forests. The forest habitat has attracted a wide range of animals, e.g. monkeys, lions, elephants, buffaloes, giraffes, leopards, water bucks and black rhinos as well as with forest vegetation.
- Deserts and semi-deserts. Deserts receive little rainfall, which is very unreliable. There is therefore very sparse vegetation that provides little food to support the wild animals. As a result, only a few small bodied animals and reptiles are found in deserts and semi-deserts.
- Lakes and rivers. These provide a habitat for some animals. The animals hide in water but feed on the surrounding vegetation or small animals. These animals include hippos, waterbuck, birds and crocodiles.
- Aquatic vegetation. Aquatic vegetation like mangrove trees, papyrus and other sea weeds grow on the shores of the sea and lakes and long river estuaries and swamps. This vegetation provides habitats for birds, sea reptiles and mammals.
- Parklands. A Parkland is dominated by grass and scattered trees which are short. These areas are enclosed by national parks and game reserves. The habitat attracts herbivores like elephants, buffaloes, giraffes, rhino and carnivores such as lions. The area also attracts birds like the ostrich, horn-bill, eagles and weaver bird.
D) Southern Somalia or Trans-Jubba regions
E) Importance’s
-
- Food: the Stone Age people and hunter-gatherers relied on wildlife, both plants and animals, for their food. In fact, some species may have been hunted to extinction by early human hunters.
- Source of employment: Wildlife provides employment to many people. Forest guarding, game rangering, office clerking and driving give employment opportunities to a large number of people.
- Pets: Monkeys and parrots are destined for the pet trade.
- Source of revenue: The government earns revenue from the license fees,
- Traditional medicines: Still other wildlife species are popular ingredients in traditional medicines sold in local markets. The medicinal value of animal parts is based largely on superstition.
2) A) Environmental hazards are events or occurrence caused by natural process or human factor that have negative effects of the natural environment.
B) * Environmental management is a process of enhancing the relationship between the environment and human being to improve the quality of both. It involves judicious and gainful utilization of natural resource for social economic development and maintenance of environmental quality.
* Environmental conservation: the wise use without wastage of our natural environment and resources, it is judicious use and protection of the natural environment.
C) Environment should manage and conserve through these reasons:
-
- To ensure the preservation of quality environment
- To prevent soil erosion through soil conservation
- To retain genetic resource since the survival of human being depend on biodiversity
- To protect water contaminated
- To protect and preserve aquatic life
- To control environmental degradation
- To control desertification
3) A) An industry is a place where raw materials like wood, mineral or clay are transformed into finished products. Industry is the production of a good or service within an economy
Industrialization is the process of developing different forms of industries most of which are associated with manufacturing.
B) Three physical factors: raw material, water, suitable climate.
Three human factors: Labor force, market, gov’t policies.
C) Significances of manufacturing industries
-
- Development of industries has led to the development of trade with other countries.
- Development of industries generates employment for the local people.
Industries lead to the growth of towns. - Industries lead to the development of infrastructure and social services in the town.
- The development of the service industry makes it possible to transport
raw materials to the factories and also distribute manufactured goods to other parts of the country. - An industry, when established in a rural area, discourages rural-urban migration because instead of people moving to urban areas away from their homes, they choose to work in a nearby industry.
- Development of an industry leads to the establishment of related industries. For example, fruit processing or meat canning leads to the development of can manufacture industries.
- The establishment of an industry based on agricultural materials leads to increased production of the raw material.
- Products of the processing industry are exported and they earn foreign exchange.as cotton, sugarcane, etc. for the industries.
4) A) Mixed farming is a growing of crops and rearing of livestock on the same farm at the same time.
B) Destination between intensive and extensive farming
| Extensive | Intensive |
| Small labor force
Yield per unit areas is low Large land is cultivated High capital per man |
High labor force
Yield per unit areas is high Small land area is cultivated Low capital per man |
C) Pastoral farming is a system of farming characterized by extensive grazing where animals exhausting pasture of a given piece of land ten they are moved to different location in search of water and pasture.
D)
-
- I) Beef farming is the rearing of cattle for meat production. Which practiced both pastoralist and subsistence farming. Some beef cattle’s are kept on ranches, farmers sell the cattle to the butcher who slaughter them, meat exports to the other African countries and Middle East.
- II) Dairy farming is the rearing of livestock for milk production. Dairy farming is one form extensive livestock farming that involves for milk production. It is carried out both large scale and small scale farms.





Recent Comments